

### Android.Vo1d Malware: A New Menace to Streaming Devices
In a worrisome update, cybersecurity experts have detected a significant malware infestation impacting close to 1.3 million streaming devices utilizing an open-source variant of Android in nearly 200 nations. The malware, dubbed **Android.Vo1d**, has compromised these devices, granting cybercriminals the ability to install further malicious software at their discretion. The infection has mainly focused on Android-operated TV boxes using outdated or unofficial firmware, raising concerns about the safety of lesser-known streaming devices.
#### What is Android.Vo1d?
Android.Vo1d is an advanced malware that has breached the system storage of streaming devices powered by Android, especially those utilizing versions of the Android Open Source Project (AOSP). In contrast to the proprietary Android TV OS, which is limited to authorized producers, AOSP is open-source and can be altered by any hardware manufacturer. This openness has rendered AOSP-based devices more susceptible to malware attacks, as they frequently run on obsolete firmware or lack the stringent security measures that Google applies to certified Android TV devices.
The malware functions by injecting malicious modules into the system storage of the compromised devices, where it can be remotely updated via command-and-control (C&C) servers overseen by the attackers. Once operational, Android.Vo1d is capable of downloading and executing supplementary malware, integrating infected devices into a larger botnet or facilitating other malicious endeavors.
#### How Does Android.Vo1d Infect Devices?
Despite thorough investigation, cybersecurity firm **Doctor Web** has not yet pinpointed the precise entry point that resulted in the infections. Nevertheless, they have suggested several plausible avenues:
1. **Exploitation of System Flaws**: One hypothesis is that the malware takes advantage of weaknesses in the operating system to obtain root access, enabling it to install itself in critical system locations.
2. **Unofficial Firmware**: An alternative theory posits that the malware was preinstalled on devices operating with unofficial or modified firmware. Numerous budget device manufacturers employ outdated Android versions and market them as current models, making them more vulnerable to recognized exploits.
3. **Supply Chain Breach**: It’s possible that the devices were compromised during the manufacturing phase, meaning they were already infected at the time of purchase by consumers.
#### Affected Devices and Firmware Versions
Doctor Web has recognized various models of TV boxes that have fallen victim to Android.Vo1d. These encompass:
| TV Box Model | Declared Firmware Version |
|——————–|———————————–|
| R4 | Android 7.1.2; R4 Build/NHG47K |
| TV BOX | Android 12.1; TV BOX Build/NHG47K |
| KJ-SMART4KVIP | Android 10.1; KJ-SMART4KVIP Build/NHG47K |
These devices operate on outdated Android versions, which are more prone to exploits. For instance, Android 7.1 became available in 2016, Android 10.1 in 2019, and Android 12.1 in 2022. Many of these units are advertised as newer editions but are, in reality, functioning on older, less secure iterations of the operating system.
#### How Android.Vo1d Functions
After Android.Vo1d breaches a device, it alters several essential system files to guarantee it can endure reboots and persist in its malicious actions. Some of the altered files include:
– **install-recovery.sh**: A script executed when the operating system initializes. The malware incorporates itself into this script to ensure it launches automatically.
– **daemonsu**: A file that grants root permissions to the malware, empowering it to modify the system.
– **debuggerd**: A system daemon generally used for error reporting. The malware replaces this file with a script that activates its malicious modules.
The primary functions of the malware are concealed in two components: **vo1d** and **wd**. These components collaboratively enable the malware to maintain its presence on the device while allowing it to download and execute further malicious programs from the C&C server. The malware can also surveil specific directories for APK files and install them automatically, broadening its capabilities.
#### Geographic Distribution of Infections
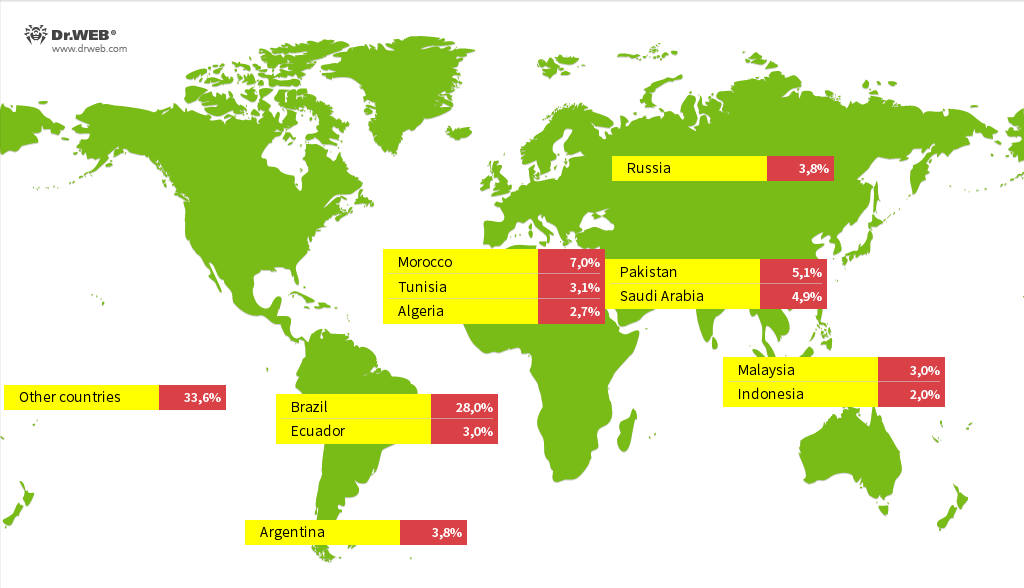
The infections have been spotted in a diverse array of countries, with the highest concentrations found in:
– Brazil
– Morocco
– Pakistan
– Saudi Arabia
– Russia
– Argentina
– Ecuador
– Tunisia
– Malaysia
– Algeria
– Indonesia
This worldwide distribution suggests that the malware does not focus on specific areas but is instead propagating indiscriminately on a global scale.
#### How to Determine if Your Device is Infected
For less tech-savvy users, identifying an infection might prove difficult without the assistance of malware detection tools. Doctor Web’s