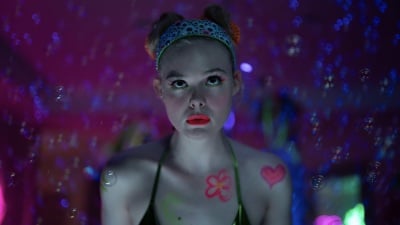Connections is a New York Times word game that’s all about finding the “common threads between words.” How to solve the puzzle.
Blog Posts
Blog Posts
A Safe Distance Review: Don’t Miss This Sexy, Sapphic Thriller
‘A Safe Distance’ review: Influenced by Patricia Highsmith, this sexy, sapphic thriller is the directorial debut of Gloria Mercer.
True Crime Meets Stoner Comedy: A Review of Cornbread Mafia Documentary
True crime meets stoner comedy in outrageous documentary “Cornbread Mafia,” which is playing at SXSW. Review.
“Margo’s Got Money Troubles Review: An Alien OnlyFans Shines in Apple’s Family Dramedy”
Elle Fanning, Michelle Pfeiffer, and Nick Offerman star in Apple TV and A24’s adaptation of Rufi Thorpe’s novel, “Margo’s Got Money Troubles.”
ST ST64UWB Cortex-M85 SoC with IEEE 802.15.4z/802.15.4ab UWB Standards and Radar Sensing
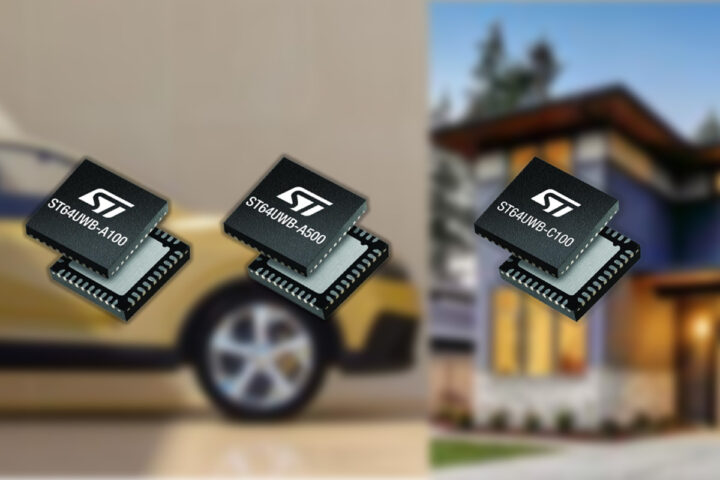

STMicroelectronics ST64UWB Arm Cortex-M85 ultra-wideband (UWB) SoC family supports both the current IEEE 802.15.4z and the upcoming IEEE 802.15.4ab UWB standards for longer-range, more reliable positioning and secure proximity-based interactions. It mainly targets digital car keys, hands-free access, and smart-device detection. The family includes the ST64UWB-A100 (automotive entry), ST64UWB-A500 (automotive premium), and ST64UWB-C100 (industrial/smart home), all built on an 18 nm FD-SOI process that improves the RF link budget by ~3 dB, yielding roughly 50% additional range beyond what IEEE 802.15.4ab alone provides. The automotive-focused A-series offers ASIL-A(B) safety support, while the ST64UWB-C100 targets consumer and commercial applications. ST64UWB family specifications: MCU Core 32-bit Arm Cortex-M85 CPU with DP-FPU, MVE, and ETM Frequency Up to 100 MHz (ST64UWB-C100, ST64UWB-A100) Up to 256 MHz (ST64UWB-A500) Memory/Storage Integrated PCM Memory SRAM and Back-up SRAM Wireless Connectivity Ultra-wideband (UWB) Radio IEEE 802.15.4z-2020 and IEEE 802.15.4ab support UWB channels 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, […]
The post ST ST64UWB Cortex-M85 ultra-wideband SoC supports IEEE 802.15.4z and 802.15.4ab UWB standards, radar sensing appeared first on CNX Software – Embedded Systems News.
Alexa+ Adds an ‘Adults Only’ Mode with Cursing, No NSFW Content
The new Sassy style can curse and roast you, but the fun ends there.
Bumble Unveils ‘Bee,’ an AI Dating Assistant
Bumble’s new AI assistant Bee will move the dating app beyond the swipe by matching people based on compatibility and goals.
The Original AirTag Is at Its Lowest Price Ever
Despite the fact Apple released a new AirTag in January, the first-generation AirTag is still a top-notch tracker if youâre embedded in Appleâs ecosystem. And right now, itâs on sale for $13.91 ($15.09 off) at Walmart, which marks a new low price. If youâre an iPhone owner, the original AirTag still delivers a level of […]
Apple to Lower App Store Commission Fees in China Starting March 15
Apple has declared a major modification to its App Store commission rates in China, commencing March 15. This move follows conversations with Chinese regulatory bodies.
Beginning on the indicated date, the commission rate for standard Apple In-App Purchase and paid app transactions will be lowered from 30% to 25%. Moreover, the commission rate for qualifying transactions under the App Store Small Business Program and Mini Apps Partner Program, along with auto-renewals of Apple In-App Purchase subscriptions after the initial year, will be reduced from 15% to 12%.
Apple has underlined that developers are not required to sign updated terms by March 15 to take advantage of these new commission rates. The company is committed to maintaining a fair and transparent app ecosystem in China, ensuring that its rates are competitive with those in other markets.
For more information, Apple has released a complete blog post detailing these updates.
“Viral Sensation: Your AI Slop Bores Me is Beyond a Joke”
The website “Your AI Slop Bores Me” has touched a nerve — now it is getting upgraded by its human creator.